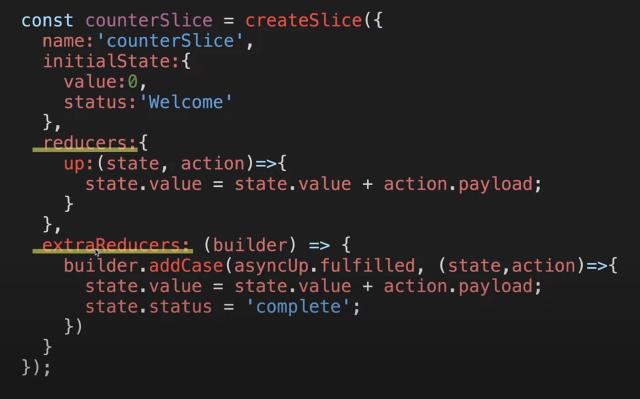
Promise
The Promise object, introduced in JavaScript ES6, was first created to solve the “callback hell” problem, which arises when callback functions accumulate during asynchronous operations.
While it works on the same principle, the Promise object provides better readability, which is why it is utilized. However, using many promise variables can lead to experiencing “promise hell” as well.
Response Time of Callback Functions, Promises, and Async/Await
The response time for both callback functions and promises is almost identical. They are read sequentially in the initial hoisting environment, causing the asynchronous part to be read before the previous processes are complete.